23 min to read
Cloth Simulation
Lab 2 of GAMES 103 Computer Animation
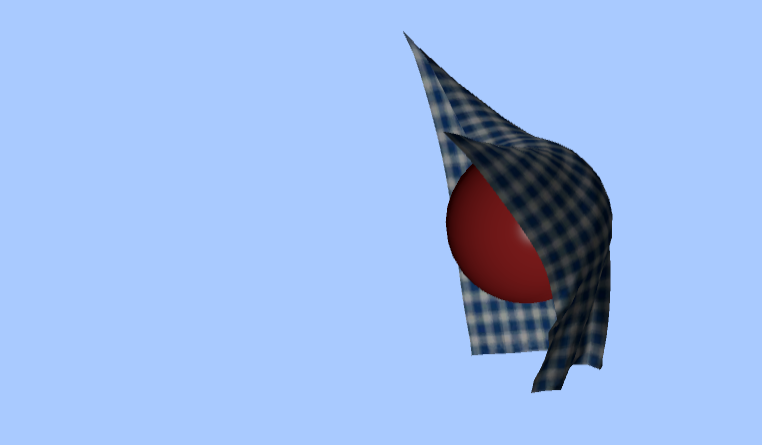
Cloth Simulation
We mainly implement the PBD method, so the completion of the assignment should be done within the PBD_model.cs script. Let’s first take a look at some of the more important arrays in the code.
Result:
float t = 0.0333f;
float damping = 0.99f;
int[] E;
float[] L;
Vector3[] V;
t represents the time length of each simulation. damping is the friction coefficient, used to simulate air resistance and the like. The E array stores the corresponding vertex indices in pairs, arranged in the order of edge lengths. For example, if the contents of the E array are {0,1,0,2,0,3}, then there are three edges in this object, formed by the vertices with indices 0 and 1, 0 and 2, 0 and 3. The L array corresponds to the length of each edge, in order corresponding to the E array. If the contents of the L array are {0.1,0.4,0.7}, then the lengths of the edges formed by the vertices with indices 0 and 1, 0 and 2, 0 and 3 are 0.1, 0.4, and 0.7, respectively. V is the velocity of each vertex.
The assignment has already helped us generate the basic vertex positions and the triangle faces in the Start function, so we can just call them directly. First, let’s look at the first question:

Based on the assignment requirements, for each vertex, we need to calculate the velocity decay, update the velocity according to gravity, and then update the position x. We can find the corresponding loop in the update function in the script to perform the update. This is similar to Lab 1:
for (int i=0; i<X.Length; i++){
if(i==0 || i==20) continue;
//Initial Setup
V[i] += t * new Vector3(0, -9.8f, 0);
V[i] *= damping;
X[i] += t * V[i];
}
Now, let’s look at question two:
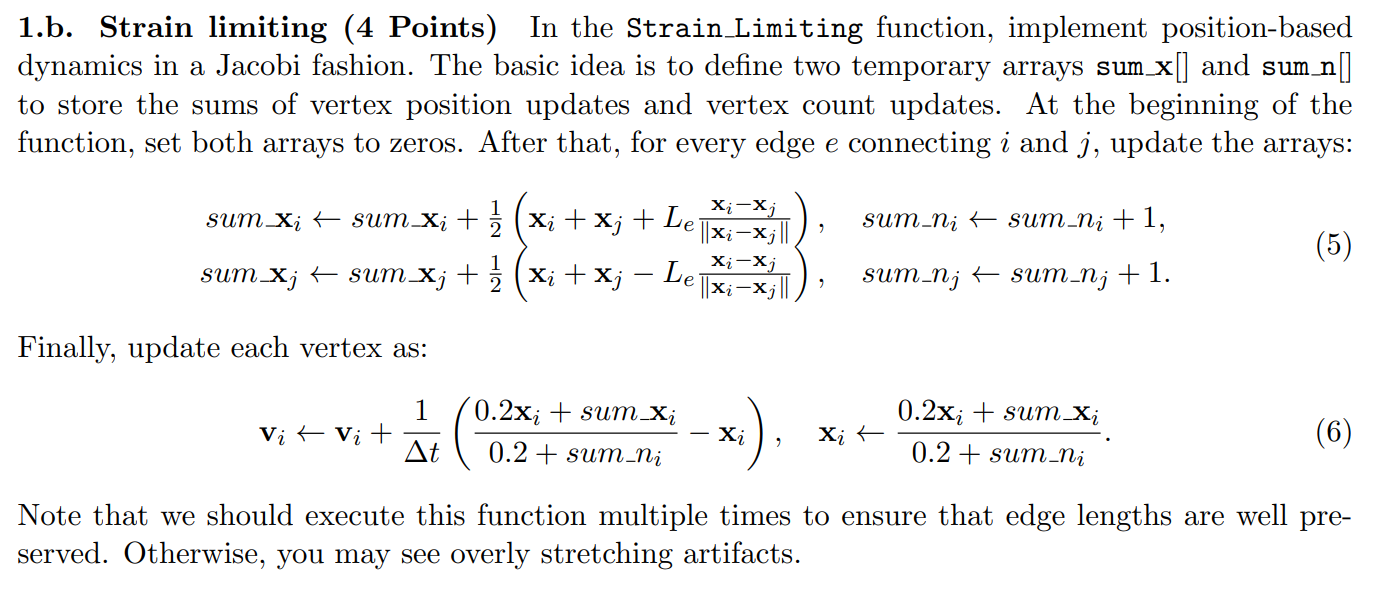
The second question is the core part of the simulation. According to the assignment requirements, we create new arrays sum_x and sum_n to store the direction of position updates for all vertices and the number of updates. Initially, set them to 0:
Vector3[] sum_x = new Vector3[vertices.Length];
float[] sum_n = new float[vertices.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++){
sum_n[i] = 0;
sum_x[i] = Vector3.zero;
}
For each edge, update sum_x and sum_n according to the formula:
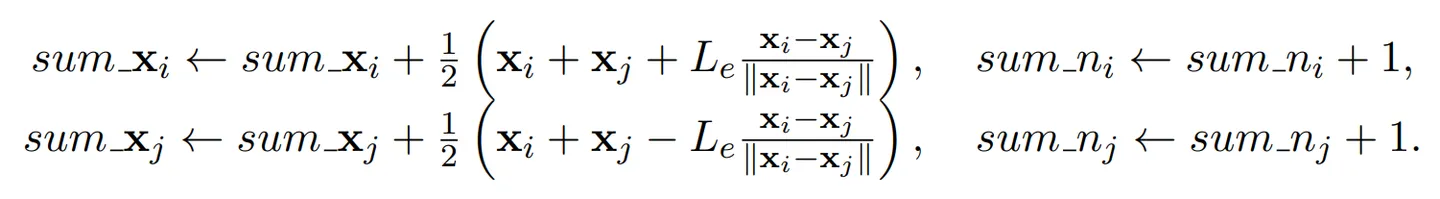
for (int e = 0; e < E.Length / 2; e++){
int i = E[e * 2 + 0];
int j = E[e * 2 + 1];
Vector3 A = vertices[i] + vertices[j];
Vector3 B = L[e] * (vertices[i] - vertices[j]).normalized;
sum_x[i] += 0.5f * (A + B);
sum_x[j] += 0.5f * (A - B);
sum_n[i]++;
sum_n[j]++;
}
An interesting point about this part of the code is that if we modify the section that updates the sum_x array, instead of using intermediate variables A and B, and write it directly as:
sum_x[i] += 0.5f * (vertices[i] + vertices[j] + L[e] * (vertices[i] - vertices[j]).normalized);
sum_x[j] += 0.5f * (vertices[i] + vertices[j] - L[e] * (vertices[i] - vertices[j]).normalized);
Writing it this way results in a significant decrease in the overall program efficiency, with a drop in fps of at least 30%. It appears that compilers struggle with complex formulas. When dealing with large formulas, it’s advisable to extract the repeated parts and create new intermediate variables to prevent redundant calculations that decrease program efficiency.
Then, update the velocity of each vertex according to the formula:
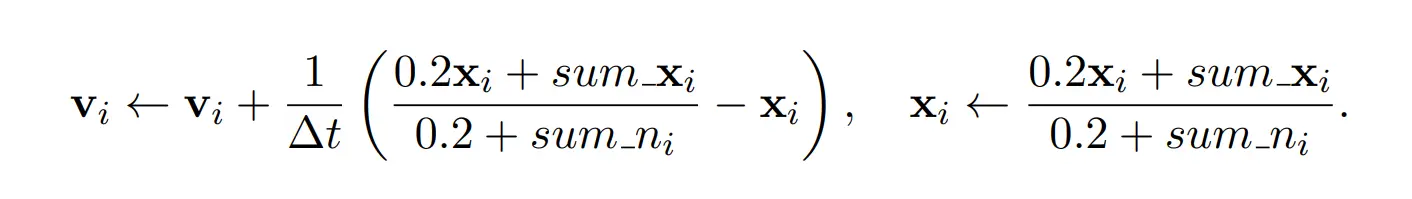
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++){
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
Vector3 A = (0.2f * vertices[i] + sum_x[i]) / (0.2f + sum_n[i]);
V[i] += (A - vertices[i]) / t;
vertices[i] = A;
}
An important detail to note in this code is to update the velocity v before updating x. Otherwise, v won’t be updated properly, as the result of the subsequent calculations will directly equal 0.
At this stage, our cloth should already be capable of undergoing some deformation. However, we’ll notice that the cloth is unable to interact with a sphere. So, next, we’ll move on to the third question, which is about refining the collision with the sphere:
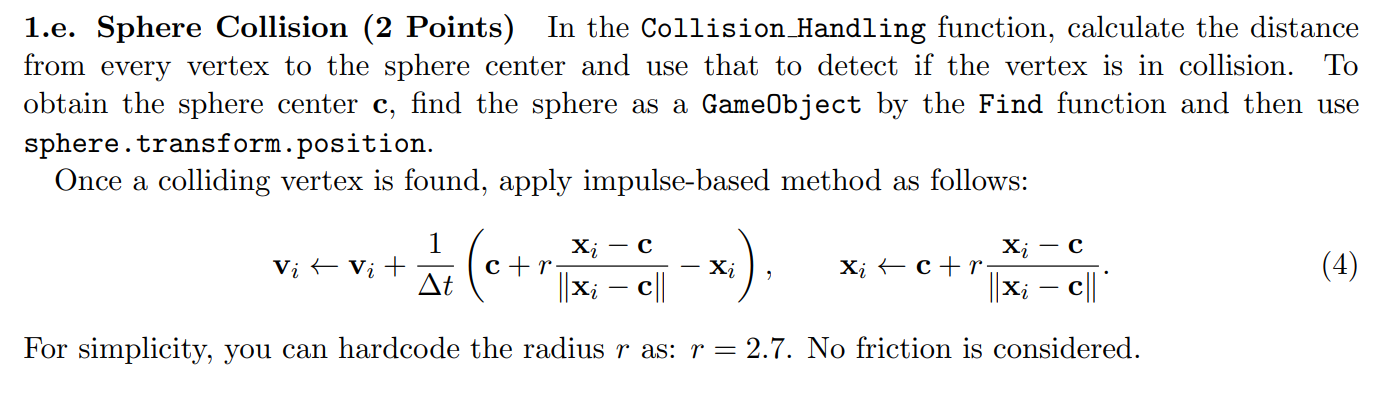
Since the collision object is a sphere, the collision detection is relatively simple. We just need to calculate the distance d **from each point to the sphere. Then, by comparing this distance with the sphere’s radius, we can determine whether a collision has occurred. If there is a collision, we then update the position and velocity of all the collision points (similar to Experiment One). The task requires us to update the Collision_Handling function, where we will add our code.
First, use Unity’s built-in find function to locate the sphere, and then get the sphere’s center coordinates, center:
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter> ().mesh;
Vector3[] X = mesh.vertices;
//For every vertex, detect collision and apply impulse if needed.
GameObject sphere = GameObject.Find("Sphere");
Vector3 center = sphere.transform.position;
Next, we calculate the distance d from each point to the sphere, keeping in mind the conversion between local and world coordinates:
float radius = 2.7f;
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++){
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
Vector3 d = transform.TransformPoint(X[i]) - center;
if (d.magnitude < radius){
Vector3 A = center + radius * d.normalized;
V[i] += (A - X[i]) / t;
X[i] = A;
}
}
mesh.vertices = X;
And with that, the task is completed! The resulting effect of the cloth simulation is as follows:

Full code is attached below for reference. Do not copy it directly to your assignment!
using UnityEngine;
using System.Collections;
public class PBD_model : MonoBehaviour
{
float t = 0.0333f;
float damping = 0.99f;
int[] E;
float[] L;
Vector3[] V;
// Use this for initialization
void Start()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
//Resize the mesh.
int n = 21;
Vector3[] X = new Vector3[n * n];
Vector2[] UV = new Vector2[n * n];
int[] T = new int[(n - 1) * (n - 1) * 6];
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
X[j * n + i] = new Vector3(5 - 10.0f * i / (n - 1), 0, 5 - 10.0f * j / (n - 1));
UV[j * n + i] = new Vector3(i / (n - 1.0f), j / (n - 1.0f));
}
int t = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < n - 1; j++)
for (int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
T[t * 6 + 0] = j * n + i;
T[t * 6 + 1] = j * n + i + 1;
T[t * 6 + 2] = (j + 1) * n + i + 1;
T[t * 6 + 3] = j * n + i;
T[t * 6 + 4] = (j + 1) * n + i + 1;
T[t * 6 + 5] = (j + 1) * n + i;
t++;
}
mesh.vertices = X;
mesh.triangles = T;
mesh.uv = UV;
mesh.RecalculateNormals();
//Construct the original edge list
int[] _E = new int[T.Length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < T.Length; i += 3)
{
_E[i * 2 + 0] = T[i + 0];
_E[i * 2 + 1] = T[i + 1];
_E[i * 2 + 2] = T[i + 1];
_E[i * 2 + 3] = T[i + 2];
_E[i * 2 + 4] = T[i + 2];
_E[i * 2 + 5] = T[i + 0];
}
//Reorder the original edge list
for (int i = 0; i < _E.Length; i += 2)
if (_E[i] > _E[i + 1])
Swap(ref _E[i], ref _E[i + 1]);
//Sort the original edge list using quicksort
Quick_Sort(ref _E, 0, _E.Length / 2 - 1);
int e_number = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < _E.Length; i += 2)
if (i == 0 || _E[i + 0] != _E[i - 2] || _E[i + 1] != _E[i - 1])
e_number++;
E = new int[e_number * 2];
for (int i = 0, e = 0; i < _E.Length; i += 2)
if (i == 0 || _E[i + 0] != _E[i - 2] || _E[i + 1] != _E[i - 1])
{
E[e * 2 + 0] = _E[i + 0];
E[e * 2 + 1] = _E[i + 1];
e++;
}
L = new float[E.Length / 2];
for (int e = 0; e < E.Length / 2; e++)
{
int i = E[e * 2 + 0];
int j = E[e * 2 + 1];
L[e] = (X[i] - X[j]).magnitude;
}
V = new Vector3[X.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
V[i] = new Vector3(0, 0, 0);
}
void Quick_Sort(ref int[] a, int l, int r)
{
int j;
if (l < r)
{
j = Quick_Sort_Partition(ref a, l, r);
Quick_Sort(ref a, l, j - 1);
Quick_Sort(ref a, j + 1, r);
}
}
int Quick_Sort_Partition(ref int[] a, int l, int r)
{
int pivot_0, pivot_1, i, j;
pivot_0 = a[l * 2 + 0];
pivot_1 = a[l * 2 + 1];
i = l;
j = r + 1;
while (true)
{
do ++i; while (i <= r && (a[i * 2] < pivot_0 || a[i * 2] == pivot_0 && a[i * 2 + 1] <= pivot_1));
do --j; while (a[j * 2] > pivot_0 || a[j * 2] == pivot_0 && a[j * 2 + 1] > pivot_1);
if (i >= j) break;
Swap(ref a[i * 2], ref a[j * 2]);
Swap(ref a[i * 2 + 1], ref a[j * 2 + 1]);
}
Swap(ref a[l * 2 + 0], ref a[j * 2 + 0]);
Swap(ref a[l * 2 + 1], ref a[j * 2 + 1]);
return j;
}
void Swap(ref int a, ref int b)
{
int temp = a;
a = b;
b = temp;
}
void Strain_Limiting()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] vertices = mesh.vertices;
//Apply PBD here.
Vector3[] sum_x = new Vector3[vertices.Length];
float[] sum_n = new float[vertices.Length];
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++)
{
sum_n[i] = 0;
sum_x[i] = Vector3.zero;
}
for (int e = 0; e < E.Length / 2; e++)
{
int i = E[e * 2 + 0];
int j = E[e * 2 + 1];
Vector3 A = vertices[i] + vertices[j];
Vector3 B = L[e] * (vertices[i] - vertices[j]).normalized;
sum_x[i] += 0.5f * (A + B);
sum_x[j] += 0.5f * (A - B);
sum_n[i]++;
sum_n[j]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < vertices.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
Vector3 A = (0.2f * vertices[i] + sum_x[i]) / (0.2f + sum_n[i]);
V[i] += (A - vertices[i]) / t;
vertices[i] = A;
}
mesh.vertices = vertices;
}
void Collision_Handling()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] X = mesh.vertices;
//For every vertex, detect collision and apply impulse if needed.
GameObject sphere = GameObject.Find("Sphere");
Vector3 center = sphere.transform.position;
float radius = 2.7f;
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
Vector3 d = transform.TransformPoint(X[i]) - center;
if (d.magnitude < radius)
{
Vector3 A = center + radius * d.normalized;
V[i] += (A - X[i]) / t;
X[i] = A;
}
}
mesh.vertices = X;
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
Mesh mesh = GetComponent<MeshFilter>().mesh;
Vector3[] X = mesh.vertices;
for (int i = 0; i < X.Length; i++)
{
if (i == 0 || i == 20) continue;
//Initial Setup
V[i] += t * new Vector3(0, -9.8f, 0);
V[i] *= damping;
X[i] += t * V[i];
}
mesh.vertices = X;
for (int l = 0; l < 32; l++)
Strain_Limiting();
Collision_Handling();
mesh.RecalculateNormals();
}
}